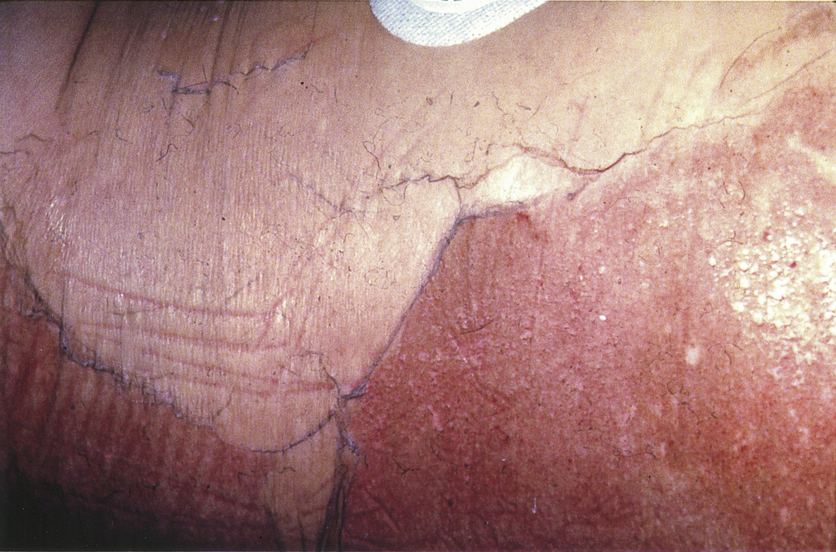
staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome (SSSS), an infection or mucous membrane colonization with toxin-producing Staphylococcus aureus. It is characterized by epidermal erythema, peeling, and necrosis, which give the skin a scalded appearance. This disorder primarily affects infants 1 to 3 months of age and children, but it may also affect adults. SSSS is more common in the newborn because of undeveloped immunity and renal systems. Treatment of SSSS commonly includes the administration of systemic antibiotics to prevent secondary infections and the replacement of body fluids to maintain fluid and electrolyte balance. Compare toxic epidermal necrolysis.