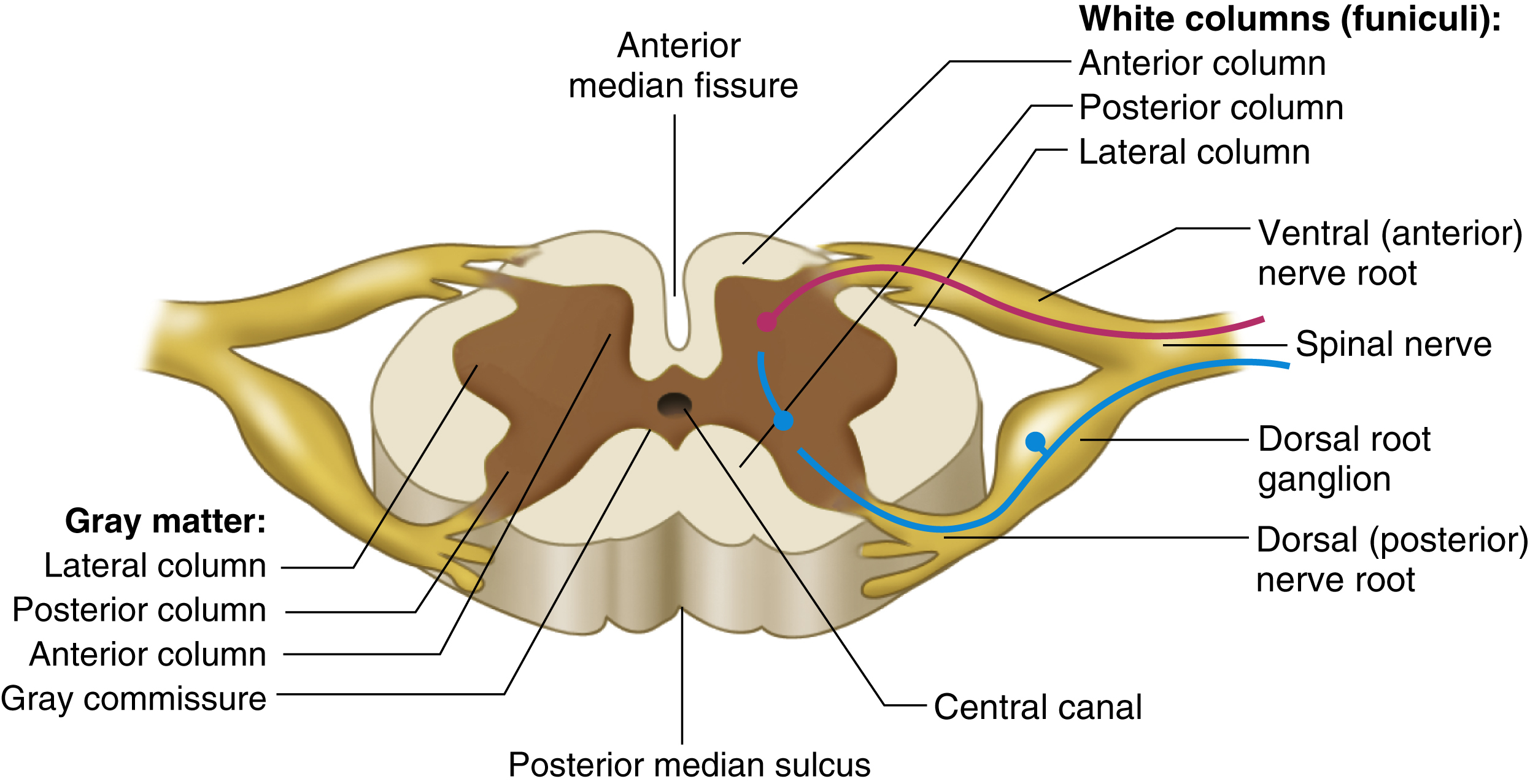
spinal cord, a long, nearly cylindric structure lodged in the vertebral canal and extending from the foramen magnum at the base of the skull to the upper part of the lumbar region. A major component of the central nervous system, the adult cord is approximately 1 cm in diameter, with an average length of 42 to 45 cm and a weight of 30 g. The cord is an extension of the medulla oblongata of the brain that extends at the level of the first or second lumbar vertebra. The cord conducts sensory and motor impulses to and from the brain and controls many reflexes. Thirty-one pairs of spinal nerves originate from the cord: 8 cervical, 12 thoracic, 5 lumbar, 5 sacral, and 1 coccygeal. It has an inner core of gray material consisting mainly of nerve cell bodies. The cord is enclosed by three protective membranes (meninges): the dura mater, arachnoid, and pia mater. Also called chorda spinalis, medulla spinalis. See also segments of spinal cord, spinal nerves.