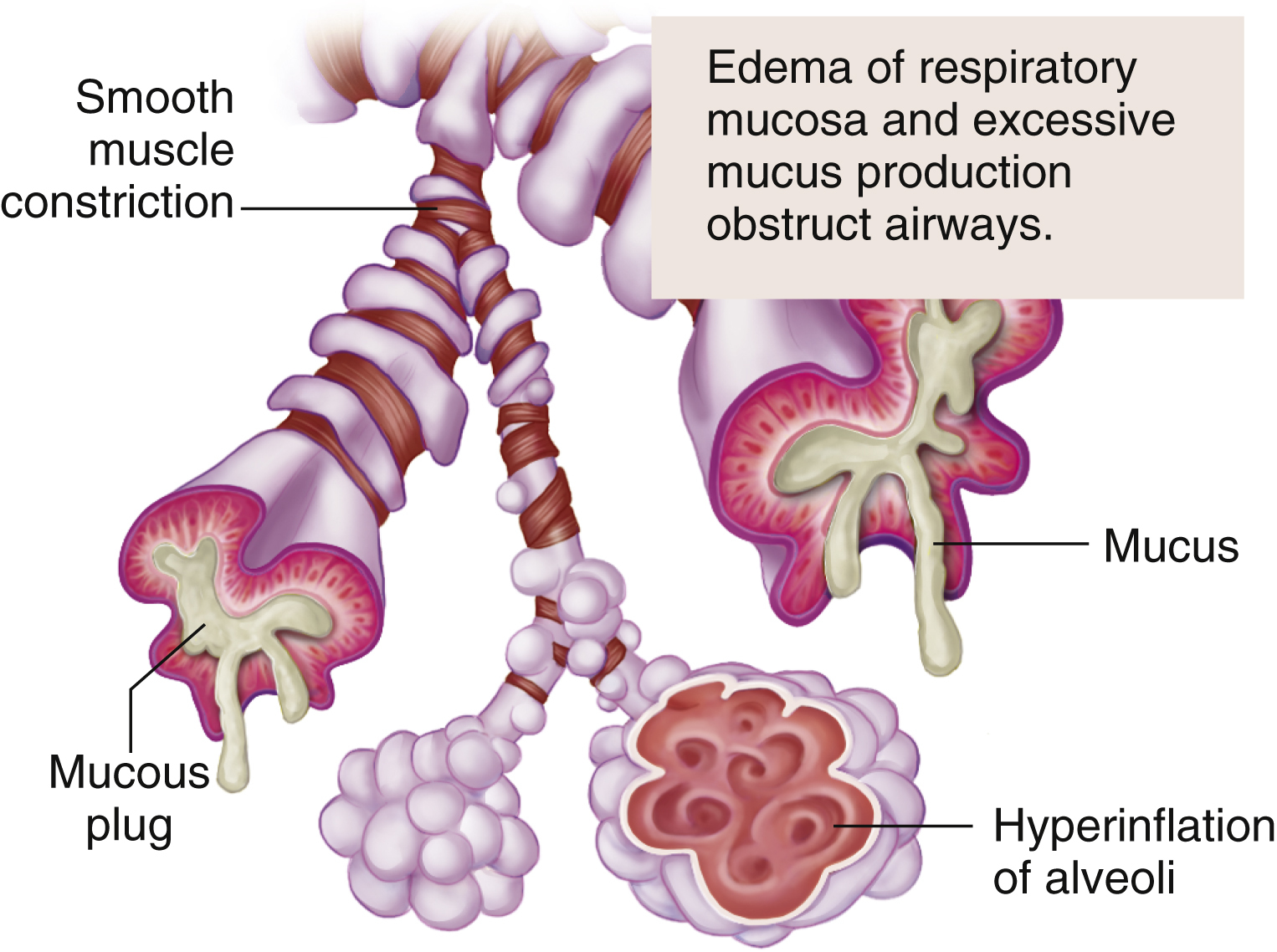
asthma /az″mə/ [Gk, panting] , a respiratory disorder causing narrowing of the airway that may be due to allergy or hypersentivity reactions. It is a complex disorder involving biochemical, immunological, infectious, endocrinological, and psychological factors. Also called bronchial asthma. See also allergic asthma, childhood asthma, exercise-induced asthma, intrinsic asthma, organic dust, status asthmaticus. ▪ OBSERVATIONS: Asthma is characterized by recurring episodes of paroxysmal dyspnea, wheezing on expiration and/or inspiration caused by constriction of the bronchi, coughing, and viscous mucoid bronchial secretions. ▪ INTERVENTIONS: Treatment may include elimination of the causative agent, hyposensitization, aerosol or oral bronchodilators, beta-adrenergic drugs, methylxanthines, cromolyn, leukotriene inhibitors, and short- or long-term use of corticosteroids. Sedatives and cough suppressants may be contraindicated. The goal of treatment is the control of symptoms and elmination of complications. ▪ PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS: The episodes may be precipitated by inhalation of allergens or pollutants, infection, cold air, vigorous exercise, or emotional stress.