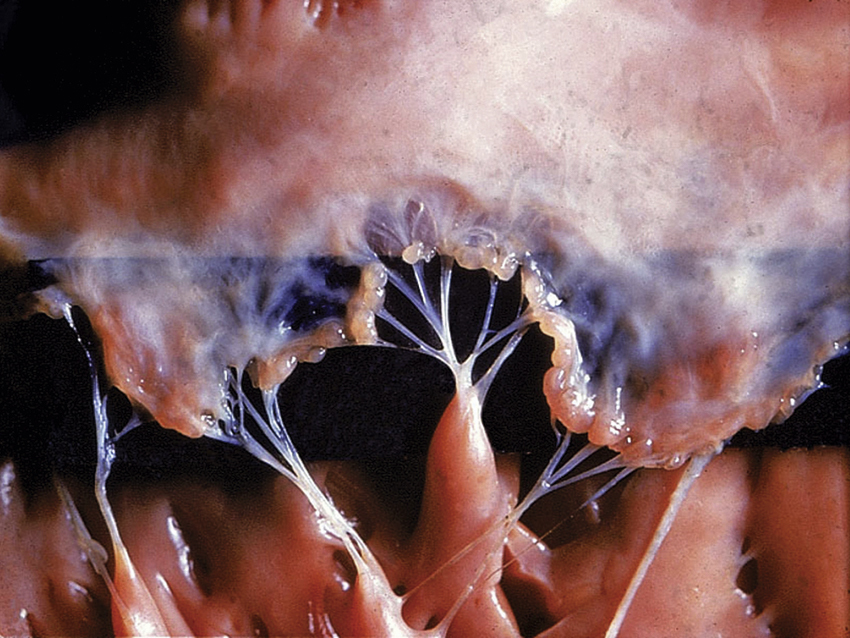
rheumatic heart disease (rhd), damage to heart muscle and heart valves caused by episodes of rheumatic fever. When a susceptible person acquires a group A beta-hemolytic streptococcal infection, an autoimmune reaction may occur in heart tissue, resulting in permanent deformities of heart valves or chordae tendineae. See also aortic stenosis, mitral valve stenosis, rheumatic fever. ▪ OBSERVATIONS: Symptoms are associated with damage to cardiac valves and may include shortness of breath and edema. A cardiac murmur may be present. ▪ INTERVENTIONS: Prevention is a priority. Prompt treatment of streptococcal infections and close follow-up for those who have experienced rheumatic fever may prevent further damage. Surgery is often required to repair or replace heart valves in patients with severely damaged valves, ▪ PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS: Involvement of the heart may be evident during acute rheumatic fever, or it may be discovered long after the acute disease has subsided.