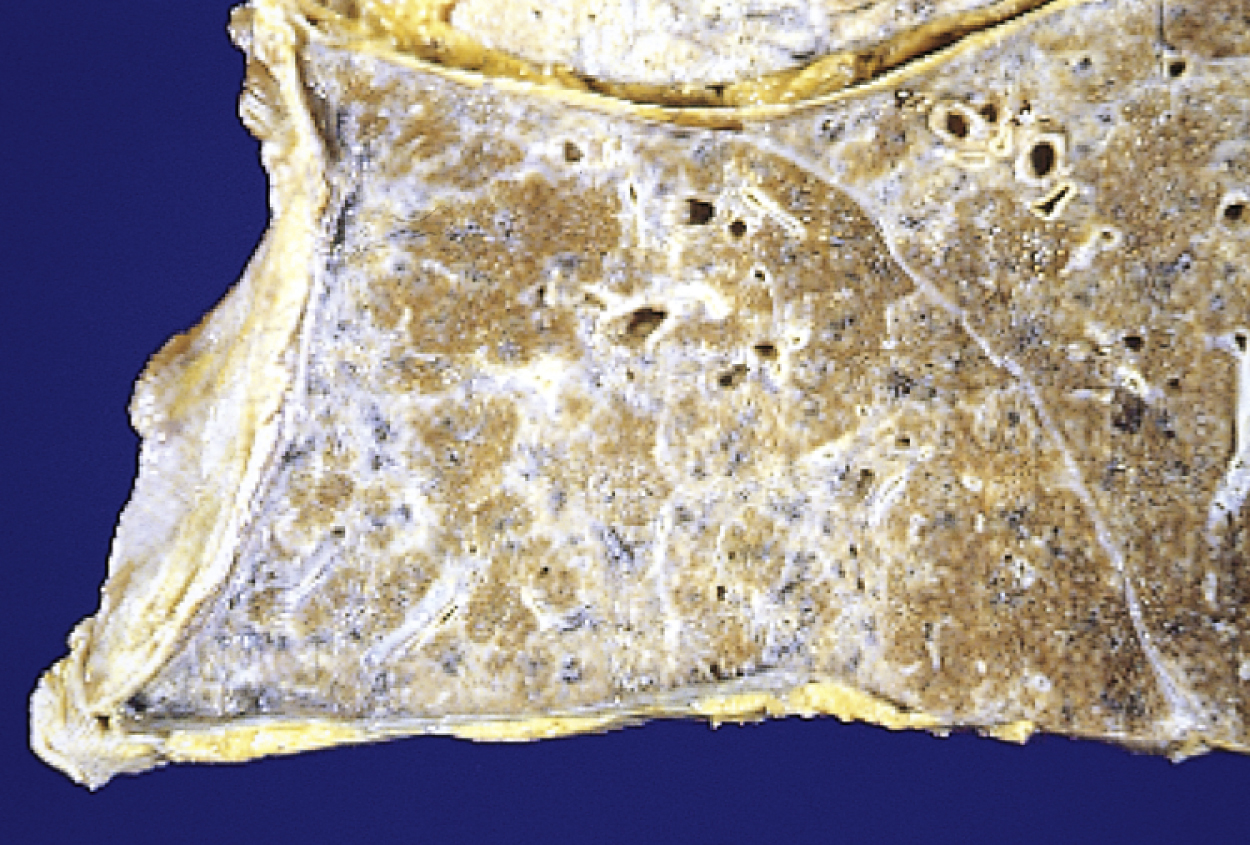
asbestosis /as-bes′-to′sis/ [Gk, asbestos, inextinguishable, osis, condition] , a chronic lung disease caused by the inhalation of asbestos fibers that results in the development of alveolar, interstitial, and pleural fibrosis. See also chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, inorganic dust. ▪ OBSERVATIONS: A comprehensive occupational and environmental history is important when asbestosis is being considered. Occupational exposure in construction, demolition, remodeling, mining, and shipbuilding increases risk, and exposure may have occurred 15 years or more before symptoms occur. Chest x-ray films show characteristic small linear opacities distributed throughout the lungs. The disease is progressive. Shortness of breath develops eventually into respiratory failure. ▪ INTERVENTIONS: Asbestosis is an irreversible condition, but treatment options do exist to increase comfort, slow the course of the disease, and assist the patient to breathe more comfortably. ▪ PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS: Cigarette smoking and continuous exposure to asbestos aggravate the condition. The risk of developing lung cancer is significantly increased. Fatal mesothelial tumors sometimes occur.