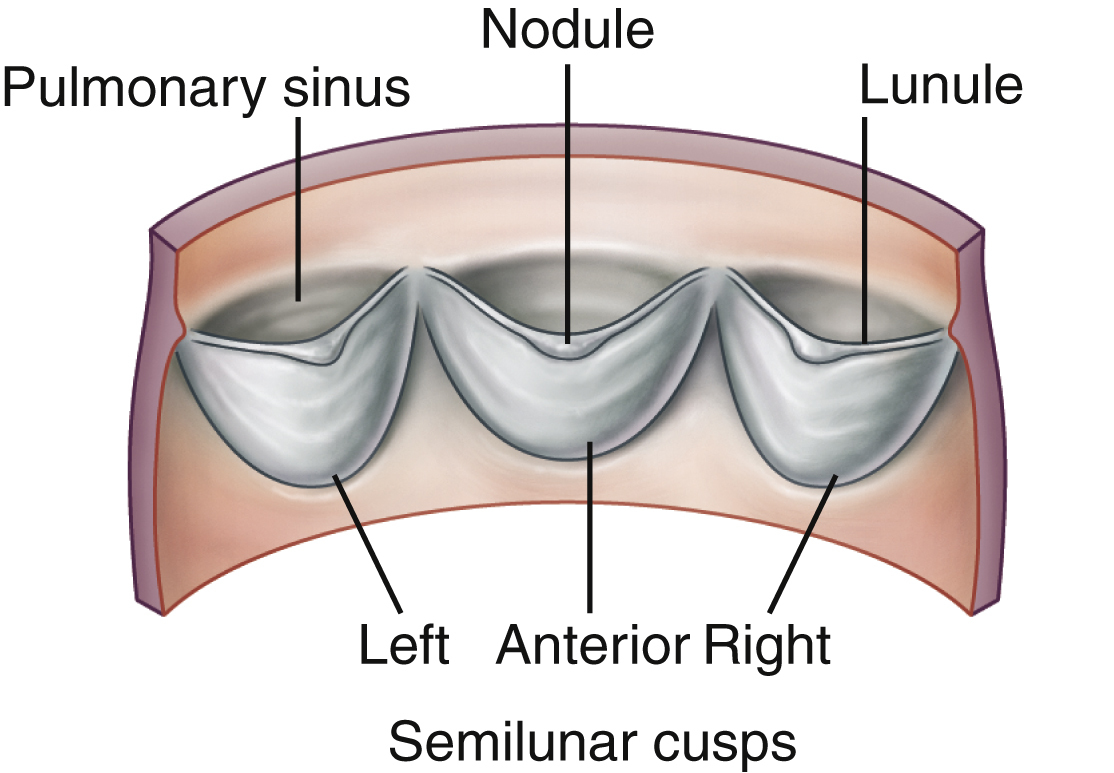
pulmonary valve, a cardiac structure composed of three semilunar cusps that close during each heartbeat to prevent blood from flowing back into the right ventricle from the pulmonary trunk. The cusps are separated by sinuses that resemble tiny buckets when they are closed and filled with blood. These flaps grow from the lining of the pulmonary trunk. When they collapse from the ejection of ventricular blood, they open the valve and allow deoxygenated blood to flow through the pulmonary artery and on to the lungs. Compare aortic valve, mitral valve, tricuspid valve.