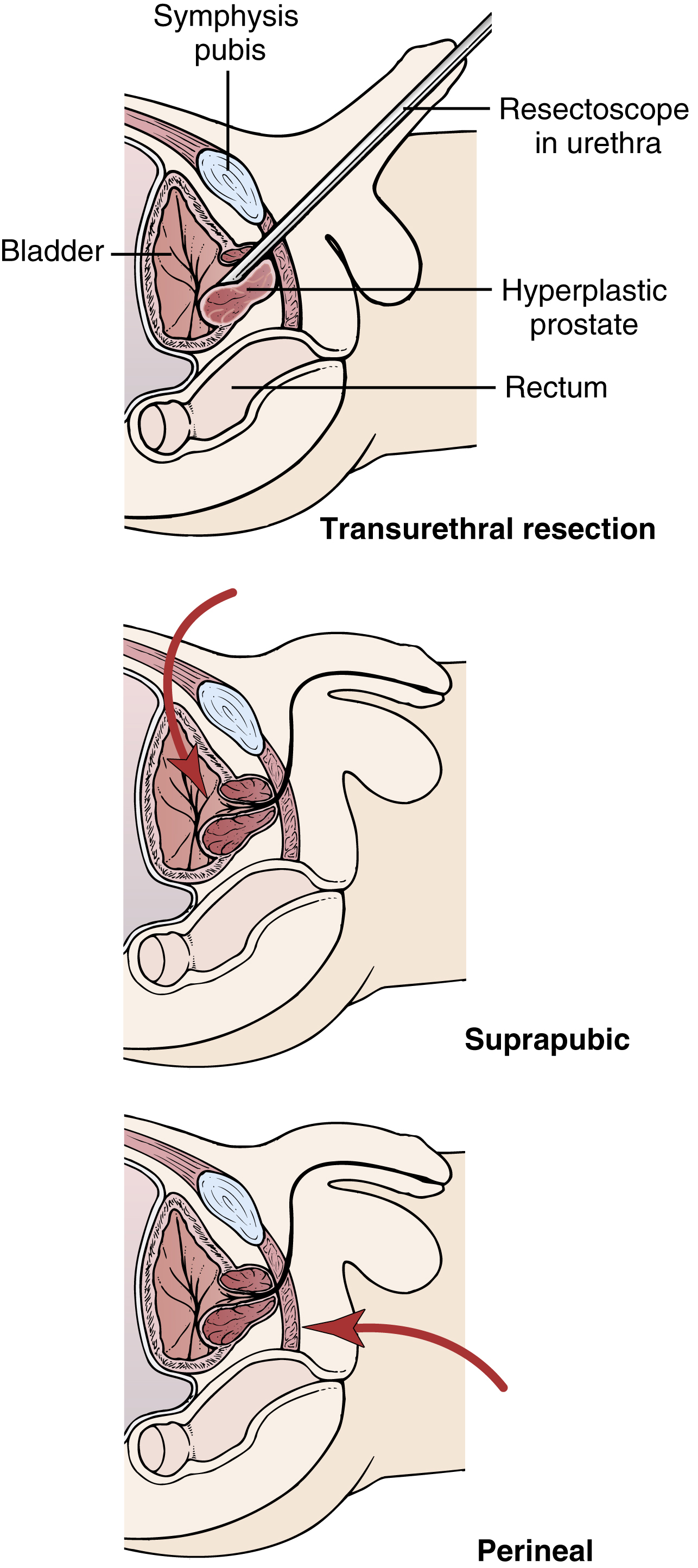
prostatectomy /pros′tətek″təmē/ [Gk, prostates + ektomē, excision] , surgical removal of a part of the prostate gland, such as that performed for benign prostatic hypertrophy, or the total excision of the gland, as performed for malignancy. Type and crossmatching of blood are done to prepare for possible transfusion. In the transurethral approach, the most common approach, a resectoscope is inserted into the urethra, and through it shavings of prostatic tissue are cut off at the bladder opening. The perineal approach is used for biopsy when early cancer is suspected or for the removal of calculi. In the suprapubic approach a large catheter is positioned into the bladder through the abdomen. Wound drains are placed in both the perineal and the suprapubic approaches. After surgery hematuria is expected for several days. Bleeding may be controlled by increasing the pressure at the balloon end of the urethral catheter. If arterial the bleeding is bright red with clots and increased viscosity and may lead to hemorrhagic shock, requiring transfusion and surgical intervention. The bladder catheter is connected to a closed system of irrigation with drainage. Meticulous aseptic technique is required to prevent infection when tending catheters, tubings, and collection bags, as well as when changing the dressing. Catheter patency is ensured, as well as care to prevent blockage or kinking of the drainage tubes. Accidental removal or dislodging of catheters is prevented. Bladder spasm may occur if a catheter becomes blocked or result from the irritation of the balloon of the catheter in the bladder. Antispasmodic drugs may prevent spasm but are not given in severe cardiac disease or if glaucoma is present. The nurse also assesses the patient’s ability to void in adequate amounts when the urethral catheter is removed. Complications of prostatectomy include urethral stricture, especially with the transurethral approach; urinary incontinence; and impotence, especially with the perineal approach.