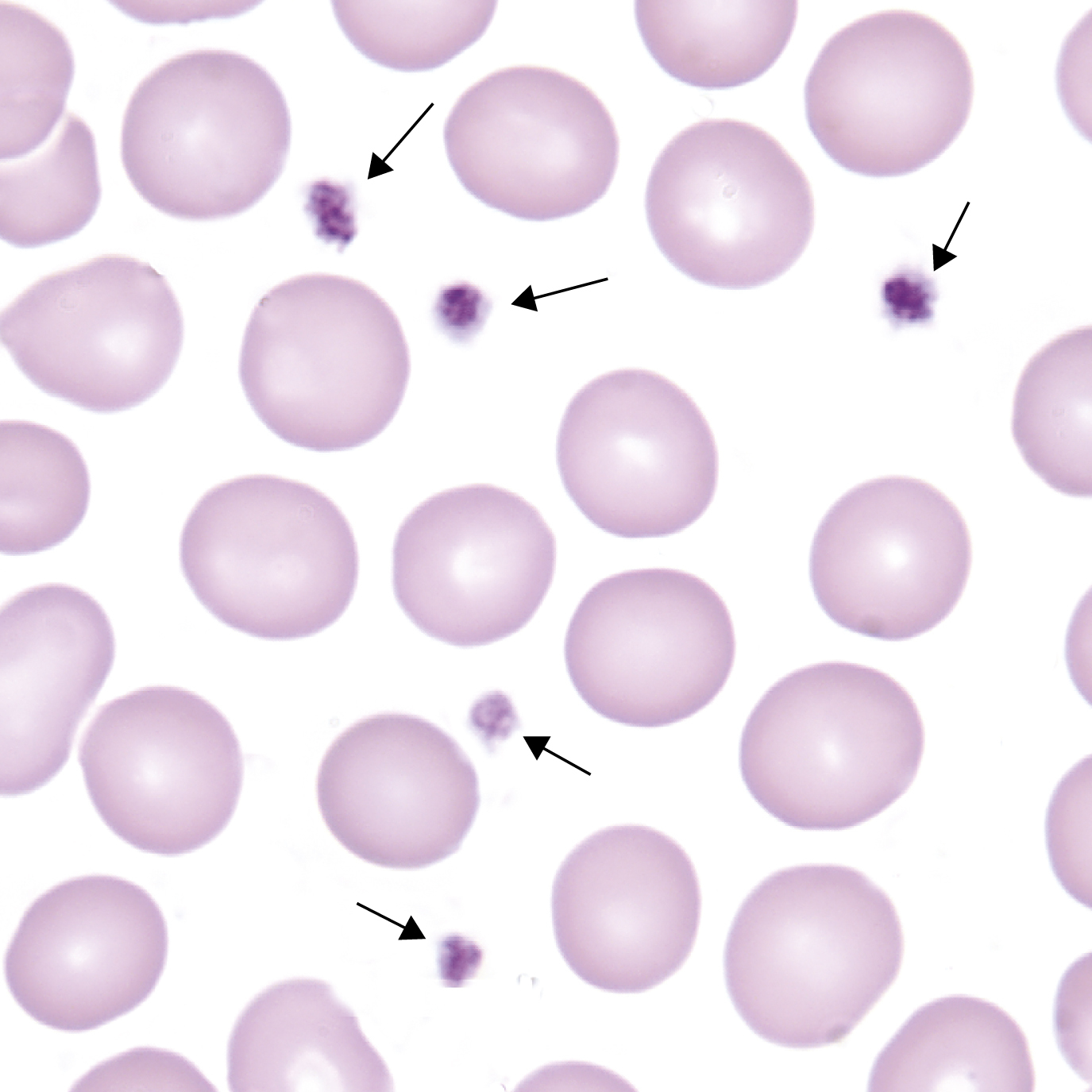
platelets /plat′lits/ [Fr, small plate] , anucleate blood cells, 1-3 μm in diameter. Platelets are formed from bone marrow megakaryocytes. Approximately one third of circulating platelets become temporarily sequestered in the spleen. Platelets are disk-shaped, contain no hemoglobin, and are essential for coagulation and in maintenance of hemostasis. The platelet count reference interval is 150,000-450,000/μL. Also called thrombocyte. Compare erythrocyte, leukocyte. See also thrombocytopenia, thrombocytosis.