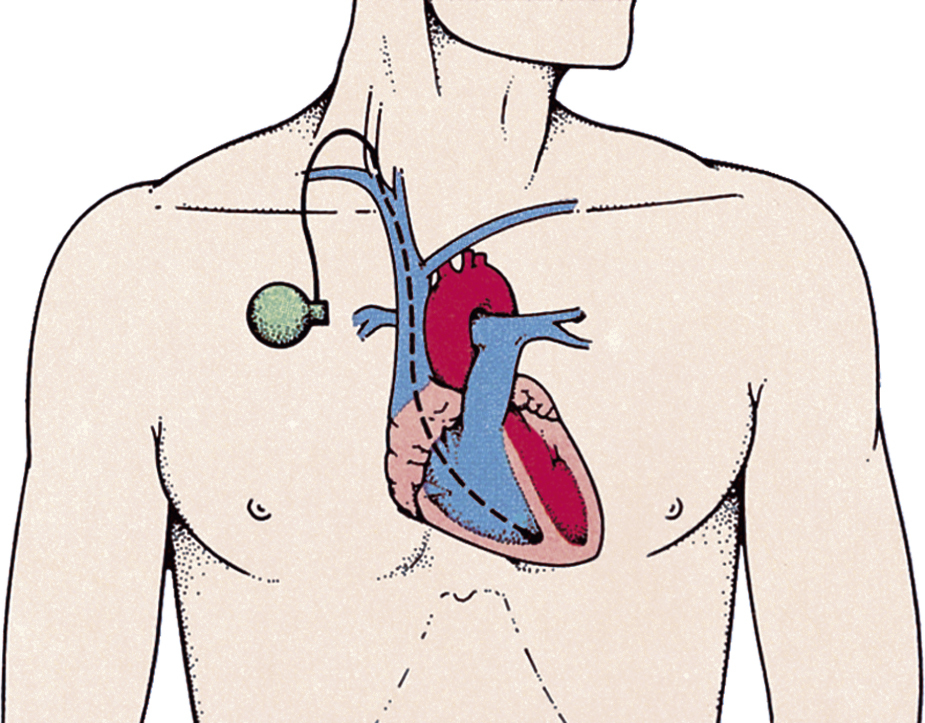
pacemaker [L, passus, step; AS, macian, to make] , 1. the sinoatrial node composed of specialized nervous tissue and located at the junction of the superior vena cava and the right atrium. It initiates the contractions of the atria, which transmit the impulse onto the atrioventricular (AV) node, thereby initiating the contraction of the ventricles. An ectopic or idioventricular pacemaker, originating in the atria, AV node, or ventricle, may cause contractions in cases of abnormal heart functioning. Also called cardiac pacemaker. 2. an electric apparatus used in most cases to increase the heart rate in severe bradycardia by electrically stimulating the heart muscle. A pacemaker may be permanent or temporary, emit the stimulus at a constant and fixed rate, or fire only on demand.