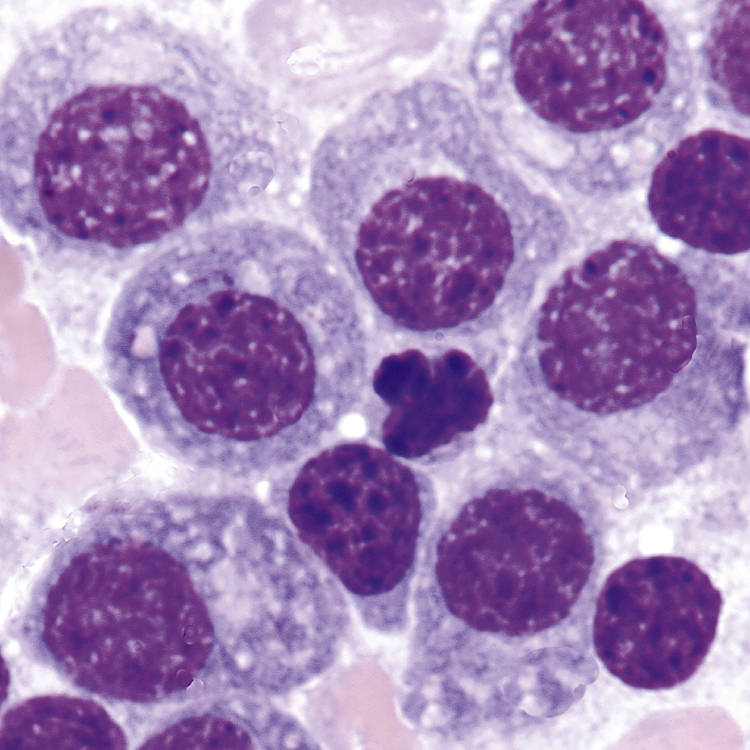
multiple myeloma, a malignant neoplasm of the bone marrow. The tumor, composed of B-lymphocyte plasma cells, disrupts normal bone marrow functions; destroys osseous tissue, especially in flat bones; and causes pain, fractures, hypercalcemia, and skeletal deformities. The onset is insidious, and most people are asymptomatic until the disease is advanced. In addition, the ability of the plasma cells to make functional antibodies decreases, leaving the person immunocompromised. Characteristically abnormal proteins in the plasma and urine, anemia, weight loss, pulmonary complications secondary to rib fractures, and kidney failure are present. The cause is unknown, but radiation and chemical exposure may increase risk. It occurs in people older than 50 years of age and is twice as common among African-Americans as Caucasians. It occurs equally in men and women. Also called multiple plasmacytoma of bone, myelomatosis, plasma cell myeloma.