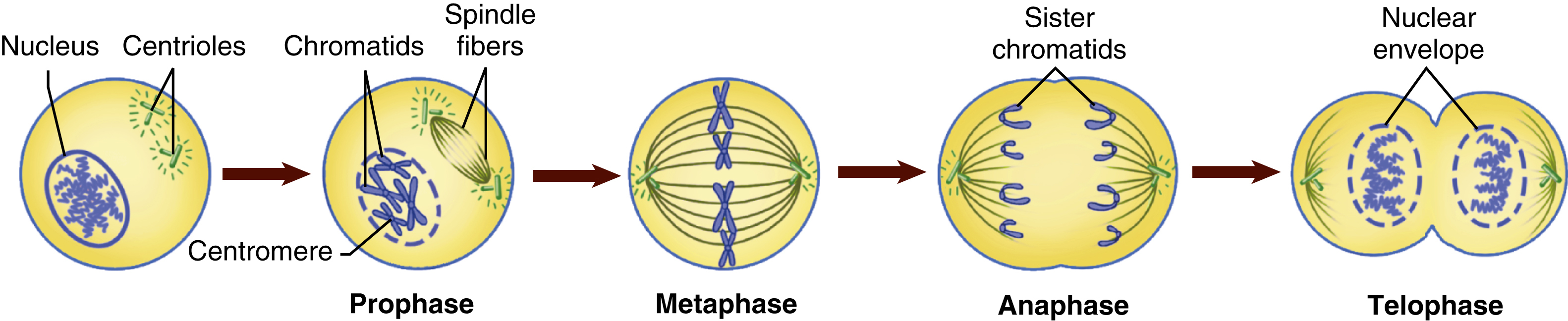
mitosis /mītō″sis, mit-/ [Gk, mitos, thread] , a type of cell division that occurs in somatic cells and results in the formation of two genetically identical daughter cells containing the diploid number of chromosomes characteristic of the species. It consists of the division of the nucleus followed by the division of the cytoplasm. The former has four stages (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase), during which the two chromatids of each chromosome separate and migrate to opposite ends of the cell. Mitosis is the process by which the body produces new cells for both growth and repair of injured tissue. Also called indirect division. Compare meiosis. Kinds include heterotypic mitosis, homeotypic mitosis, multipolar mitosis, pathological mitosis. See also interphase. −mitotic, adj.