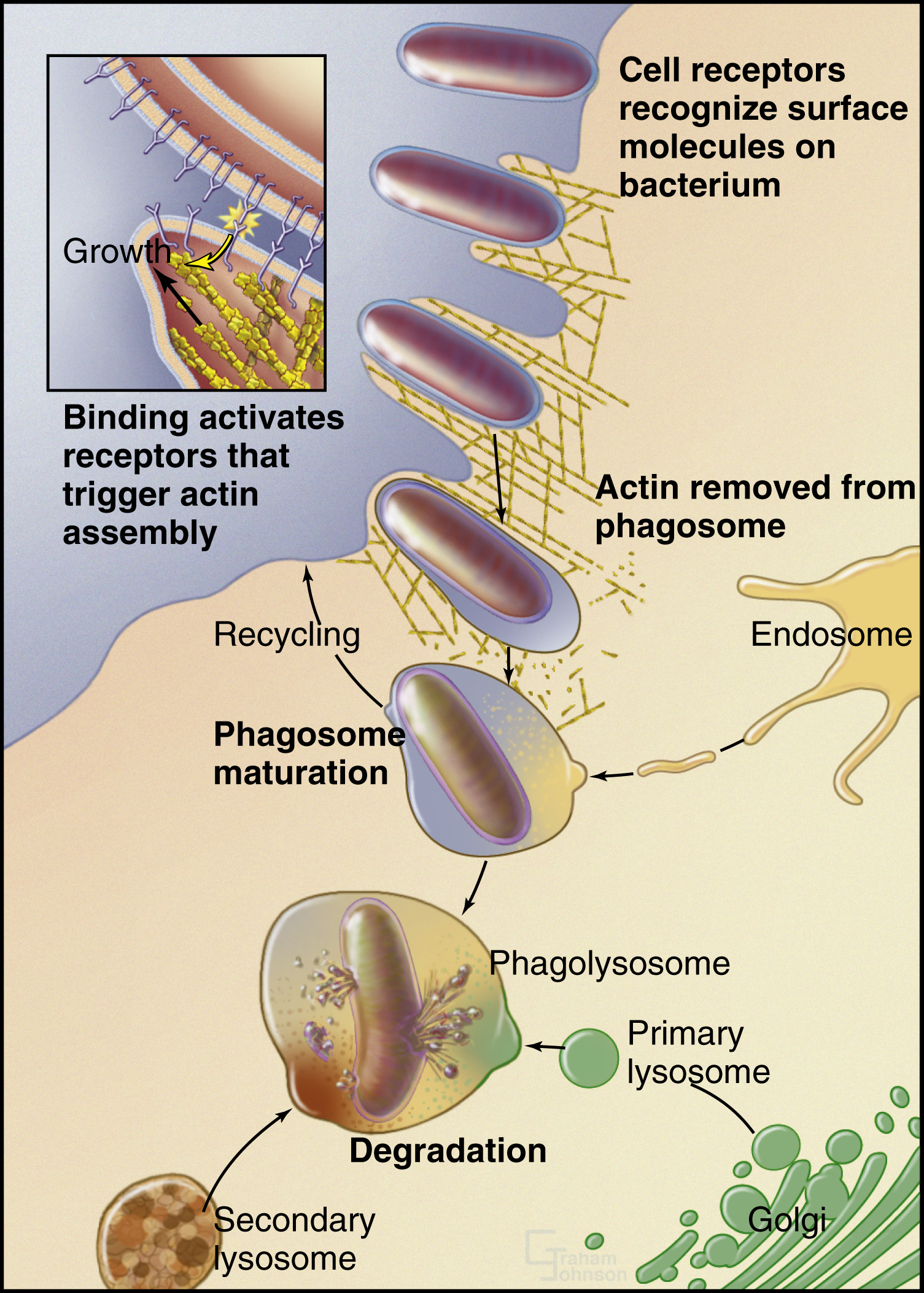
macrophage /mak″rəfāj/ [Gk, makros + phagein, to eat] , a granular mononuclear phagocyte that circulates as a monocyte in the blood and resides in all tissues. Macrophages recognize and engulf foreign materials and present fragments or epitopes on their membranes to initiate an immune response. Macrophages have many names, including histiocytes, reticuloendothelial cells, Kupffer cells in the liver, and littoral cells in the spleen. Macrophages are the single most abundant cell in the human body, more numerous than skin cells or red blood cells. See also Kupffer cells, phagocyte, reticuloendothelial system.