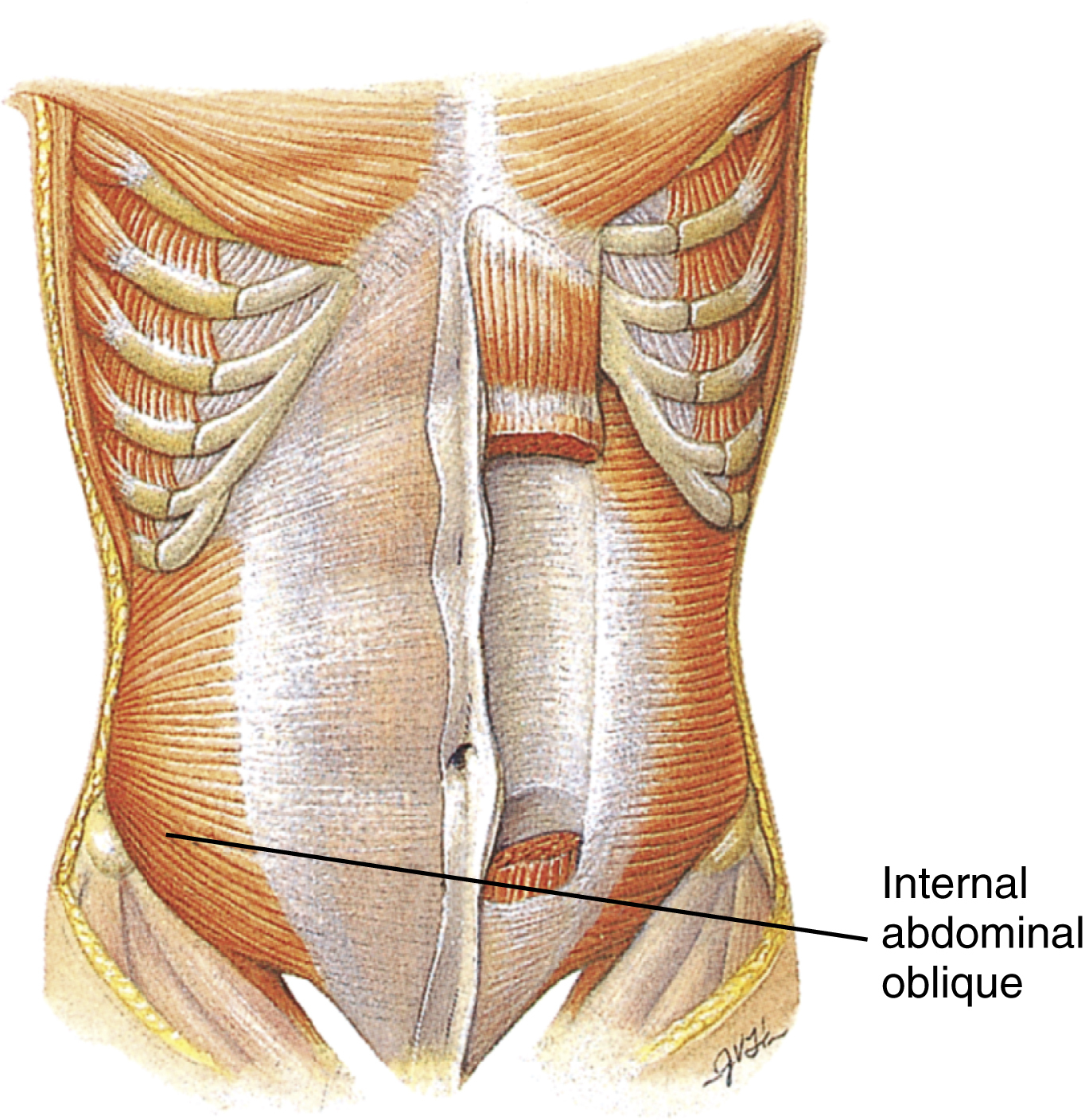
internal abdominal oblique muscle, one of a pair of anterolateral muscles of the abdomen, lying under the external oblique muscle in the lateral and ventral part of the abdominal wall. It is smaller and thinner than the external oblique muscle. It functions to compress the abdominal contents and assists in micturition, defecation, emesis, parturition, and forced expiration. Both muscles acting together serve to flex the vertebral column, drawing the costal cartilages toward the pubis. One side acting alone bends the vertebral column laterally and rotates it, drawing the shoulder of the opposite side downward. Also called obliquus internus abdominis. Compare external abdominal oblique muscle.