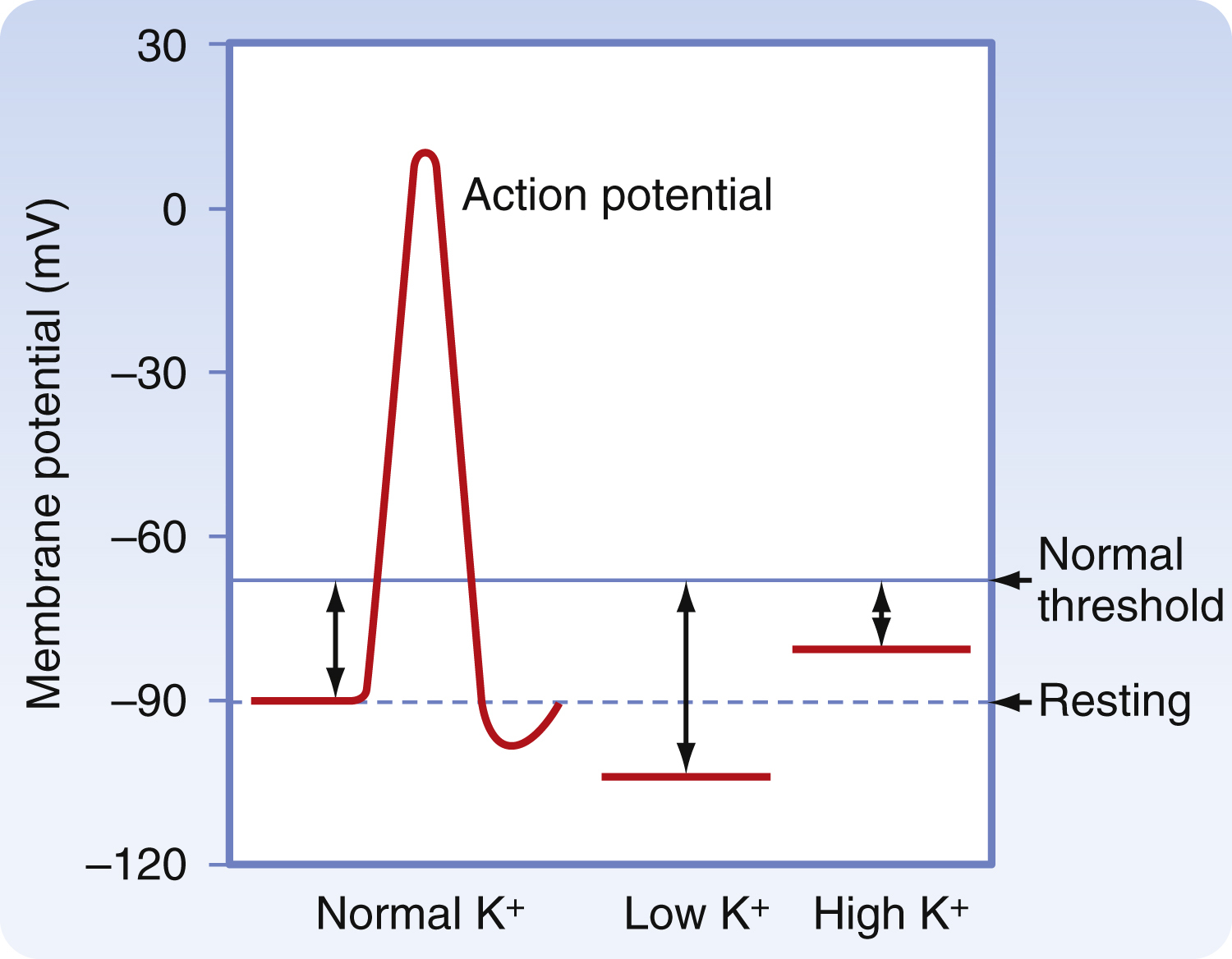
hypokalemia /hī′pōkəlē″mē·ə/ [Gk, hypo + L, kalium, potassium; Gk, haima, blood] , a condition in which an inadequate amount of potassium, the major intracellular cation, is found in the circulating bloodstream. Hypokalemia is characterized by abnormal electrocardiographic findings, weakness, confusion, mental depression, and flaccid paralysis. The cause may be starvation, treatment of diabetic acidosis, adrenal tumor, or diuretic therapy. Mild hypokalemia may resolve itself when the underlying disorder is corrected. Severe hypokalemia may be treated by the administration of potassium chloride, orally or parenterally, and by a diet high in potassium. Also called kaliopenia. Also spelled hypokalaemia. Compare hyperkalemia. See also electrolyte balance. −hypokalemic, adj.