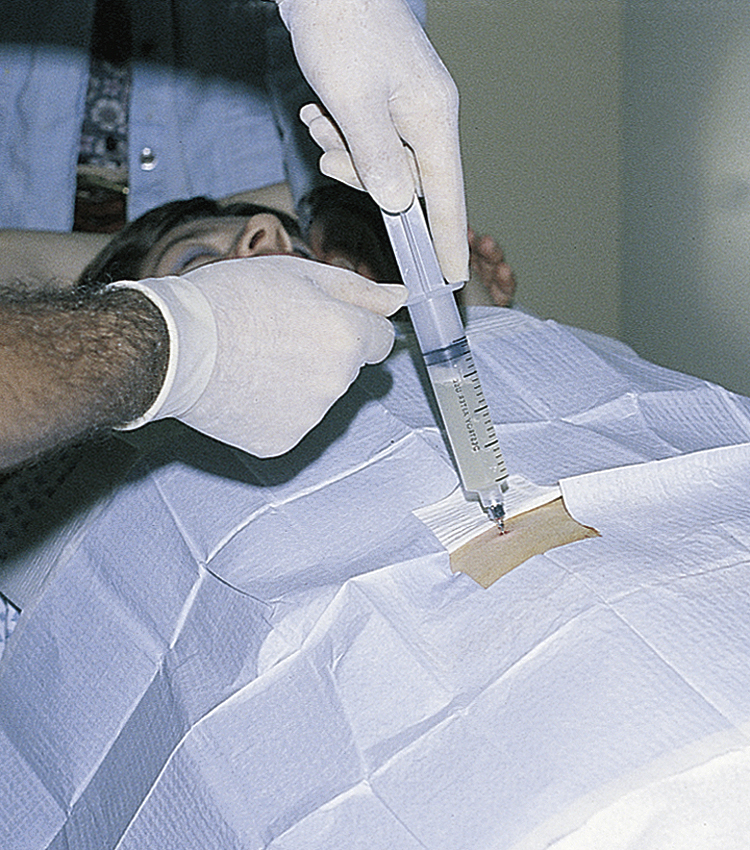
amniocentesis /am′nē·ōsentē″sis/ [Gk, amnos, lamb’s caul, kentesis, pricking] , an obstetric procedure in which a small amount of amniotic fluid is removed for laboratory analysis. ▪ METHOD: With the use of ultrasound imaging techniques, the position of the fetus and the location of the placenta are determined. The skin on the mother’s abdomen is aseptically prepared, and a local anesthetic is usually injected. A needle attached to a syringe is introduced into a part of the uterus where there is the least chance of perforating the placenta or scratching the fetus. Between 20 and 25 mL of amniotic fluid is aspirated. Amniocentesis is performed to diagnose various inherited disorders, including chromosomal aberrations, neural tube defects, and Tay-Sachs disease. It is also performed to discover the sex of the fetus if certain sex-linked disorders are suspected. Later in pregnancy, amniocentesis may be performed to assess fetal lung maturity by testing the lecithin/sphingomyelin ratio and the presence of phosphatidyl-glycerol in the laboratory before elective delivery or for evidence of infection (chorioamnionitis). ▪ PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS: A woman must sign an informed consent form before amniocentesis. Specifically stated in the consent form are the reasons for performing the procedure and the facts that fluid is to be removed after needle puncture of the uterus, that ultrasound imaging techniques are usual adjuncts, that the procedure may fail to give the results intended, and that spontaneous abortion, nausea, abdominal pain, or fetal injury may occur. The woman is reassured that complications and failure are rare; she is given emotional support before, during, and after the procedure. In testing for inherited disorders, 10 days to 2 weeks is usually necessary for tissue culture before a diagnosis may be made; this waiting period may be extremely stressful for the mother. The woman is warned to report any signs of infection or of the onset of labor. Rho(D) immunoglobulin should be given to pregnant women who are Rh negative.