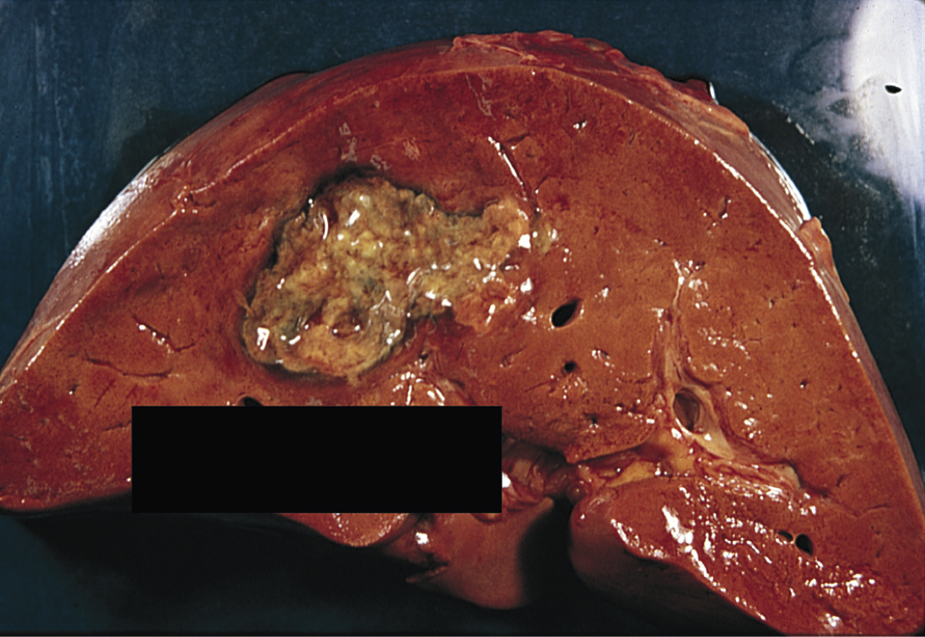
amebic abscess /əmē″bik/ , a collection of pus formed by disintegrated tissue in a cavity, usually in the liver, caused by Entamoeba histolytica. Cysts of the organism, ingested in fecally contaminated food or water, pass into the intestine, where active trophozoites are released. The trophozoites enter the intestinal mucosa, causing ulceration, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and severe diarrhea, and they may invade the liver and produce an abscess. Oral metronidazole and oral or intramuscular chloroquine hydrochloride are used to treat hepatic amebic abscesses. See also amebiasis.