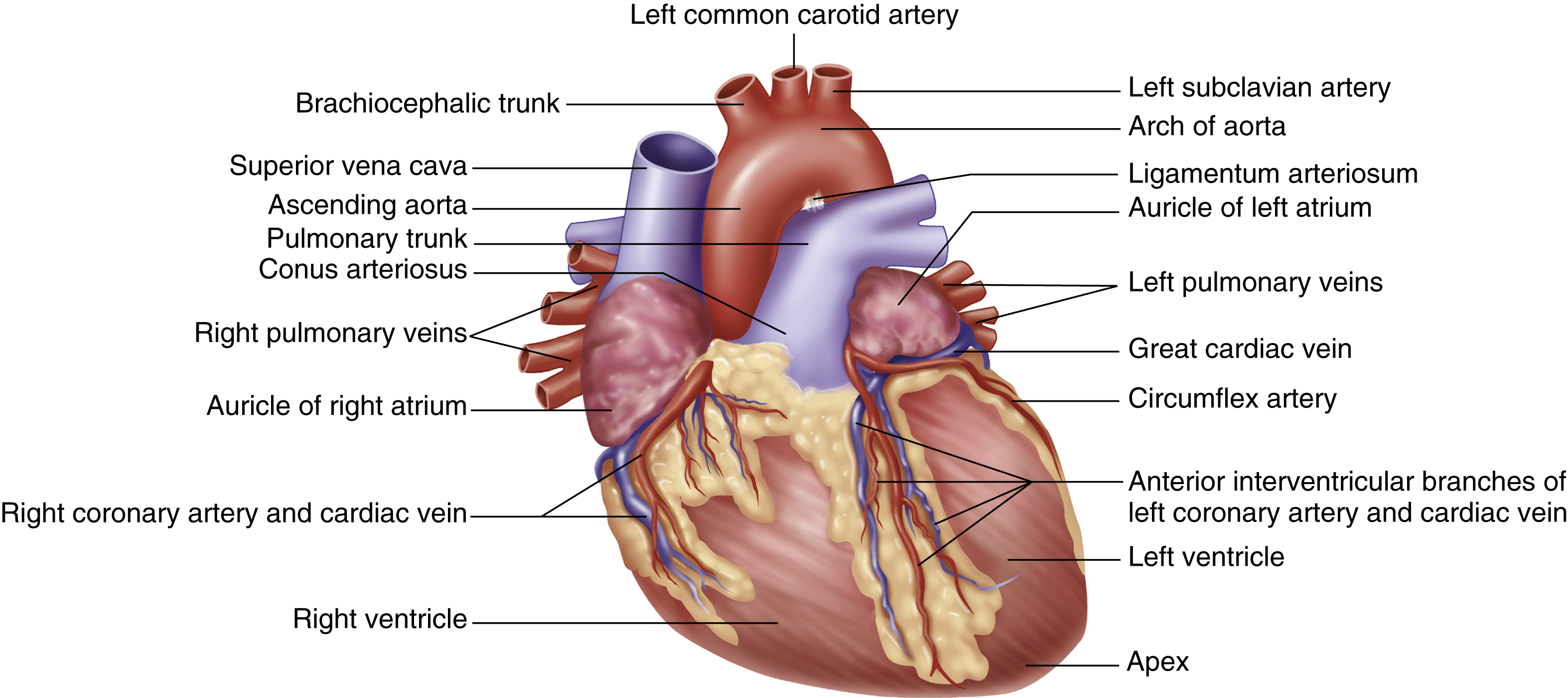
heart [AS, heorte] , the muscular cone-shaped hollow organ, about the size of a clenched fist, that pumps blood throughout the body and beats normally about 70 times per minute by coordinated nerve impulses and muscular contractions. Enclosed in pericardium, it rests on the diaphragm between the lower borders of the lungs, occupying the middle of the mediastinum. It is covered ventrally by the sternum and the adjoining parts of the third to the sixth costal cartilages. The organ is about 12 cm long, 8 cm wide at its broadest part, and 6 cm thick. The weight of the heart in men averages between 280 and 340 g and in women, between 230 and 280 g. The layers of the heart, starting from the outside, are the epicardium, the myocardium, and the endocardium. The chambers include two ventricles with thick muscular walls, making up the bulk of the organ, and two atria with thin muscular walls. A septum separates the ventricles and extends between the atria (interatrial septum), dividing the heart into the right and the left sides. The left side of the heart pumps oxygenated blood into the aorta and on to all parts of the body. The right side receives deoxygenated blood from the vena cava and pumps it into the pulmonary arteries. The valves of the heart include the tricuspid valve, the bicuspid (mitral) valve, the semilunar aortic valve, and the semilunar pulmonary valve. The sinoatrial node in the right atrium of the heart (under the control of the medulla oblongata in the brainstem) initiates the cardiac impulse, causing the atria to contract. The atrioventricular (AV) node near the septal wall of the right atrium spreads the impulse over the AV bundle (bundle of His) and its branches, causing the ventricles to contract. Both atria contract simultaneously, followed quickly by the simultaneous contraction of the ventricles. The sinoatrial node of the heartbeat sets the rate. Other factors affecting the heartbeat are emotion, exercise, hormones, temperature, pain, and stress. See also endocardium, epicardium, heart valve, myocardium.