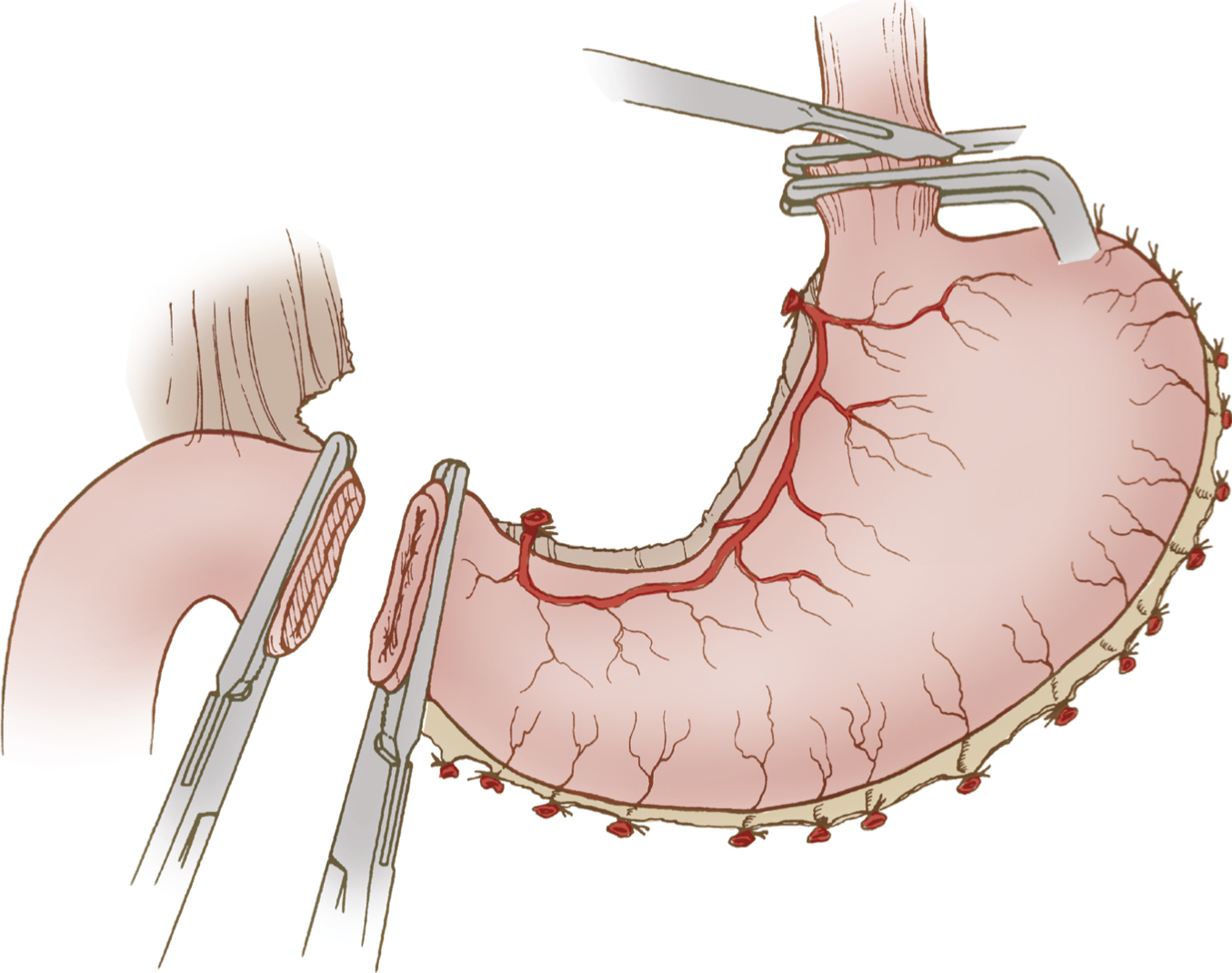
gastrectomy /gastrek″təmē/ , surgical excision of all or, more commonly, part of the stomach, performed to remove a chronic peptic ulcer, to stop hemorrhage in a perforating ulcer, or to remove a malignancy. Before surgery a GI series is done and a nasogastric tube is inserted. With the patient under general anesthesia, one half to two thirds of the stomach is removed, including the ulcer and a large area of acid-secreting mucosa. A gastroenterostomy is then done, joining the remainder of the stomach to the jejunum or duodenum. After surgery the nurse observes the drainage from the nasogastric suction tube for bright red blood, indicative of hemorrhage. Blockage of the tube is reported at once, because gastric distension strains the suture lines. Irrigation is done only according to surgeon’s orders, gently and with small amounts of fluid, if at all. Adequate medication for pain allows deeper breathing and coughing because the incision is close to the diaphragm. The nurse encourages the patient to breathe deeply and, if necessary, to cough. With the return of peristalsis, water is given orally, and, if tolerated without pain or nausea, the nasogastric tube is removed. The diet gradually progresses to six small bland meals a day with 120 mL of fluid hourly between meals. A temperature elevation or dyspnea may indicate leakage of oral fluids or gastric leaks from the incision around the anastomosis. The most common complication of gastrectomy is dumping syndrome, with fullness and discomfort after meals. Other possible complications include marginal peptic ulcer, in which gastric acids come into contact with a suture line; afferent loop syndrome, in which the duodenal loop is blocked and pancreatic juices and bile flow back into the stomach; vitamin B12 and folic acid deficiency; reduced absorption of calcium and vitamin D; and functional hyperinsulinism, in which carbohydrates now passing directly into the small bowel cause an outpouring of insulin into the bloodstream and a resultant hypoglycemia within 2 hours. See also dumping syndrome, gastric resection, gastroenterostomy, nasogastric tube, peptic ulcer.