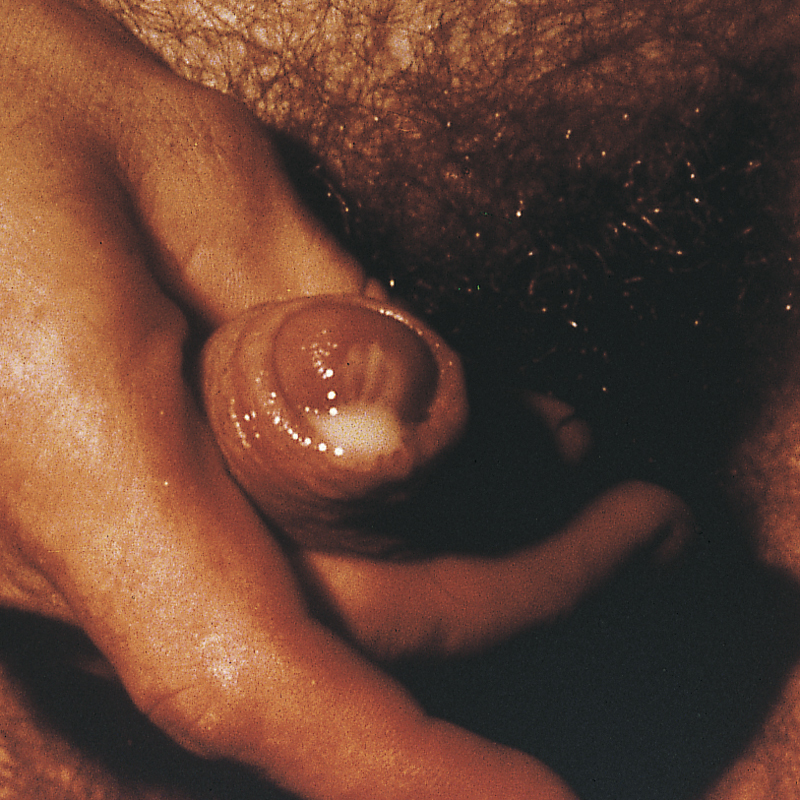
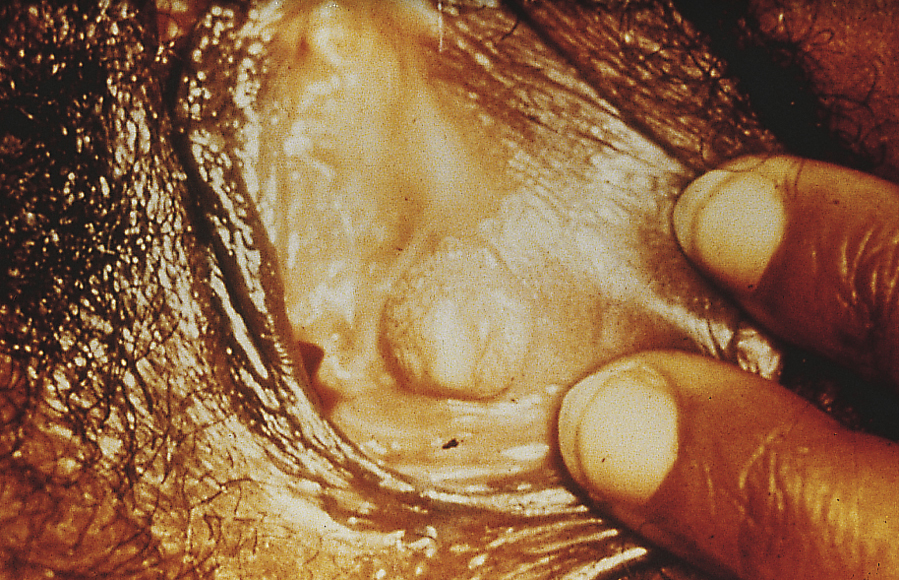
gonorrhea /gon′ərē″ə/ [Gk, gone + rhoia, flow] , a common sexually transmitted disease that most often affects the genitourinary tract and occasionally the pharynx or rectum. Infection results from contact with an infected person or with secretions containing the causative organism Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Infants born to infected women may acquire conjunctival infection from passage through the birth canal. Gonorrheal infections must be reported to local health departments in the United States. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention estimate that more than 700,000 new infections occur annually. Also spelled gonorrhoea. ▪ OBSERVATIONS: Urethritis; dysuria; purulent, greenish-yellow urethral or vaginal discharge; red or edematous urethral meatus; and itching, burning, or pain around the vaginal or urethral orifice are characteristic. The vagina may be massively swollen and red, and the lower abdomen may be tense and very tender. As the infection spreads, as occurs more commonly in women than in men, nausea, vomiting, fever, and tachycardia may occur as salpingitis, oophoritis, or peritonitis develops. Inflammation of the tissues surrounding the liver also may occur, causing pain in the upper right quadrant of the abdomen. Severe disseminated infection is also more common in women than in men and is characterized by signs of septicemia with polyarthritis, tender papillary lesions on the skin of the hands and feet, and inflammation of the tendons of the wrists, knees, and ankles. Gonococcal ophthalmia involves infection of the conjunctiva and may lead to scarring and blindness. Gonorrhea is diagnosed by bacteriological culture of the organism from a smear obtained from a specimen of exudate. In men a microscopic study of a Gram’s-stained specimen of exudate that reveals gram-negative intracellular diplococci is diagnostic of gonorrheal infection, but this finding is not diagnostic in women. ▪ INTERVENTIONS: The recommended regimen for uncomplicated gonorrhea is ceftriaxone, 125 mg, intramuscularly once or doxycycline, 100 mg, orally twice daily for 7 days. Generally patients with gonorrhea infections should be treated simultaneously for presumptive chlamydial infections. Alternative medications are ciprofloxacin, ofloxacin, cefixime, and azithromycin. Treatment failure of this regimen is rare; therefore a follow-up culture for test of cure is not essential. The routine instillation of 1% solution of silver nitrate or topical ophthalmic antibiotic into the eyes of the newborn provides effective prophylaxis against conjunctival infection in the newborn period that might otherwise result from contact with the infected secretions of an asymptomatic infected mother during vaginal delivery. ▪ PATIENT CARE CONSIDERATIONS: It is important that the patient’s sexual contacts be treated. Before administration of any antibiotic it is ascertained that the patient does not have any known sensitivity to the drug being given and that equipment and drugs are available to treat any hypersensitivity reaction that may occur. Precaution against spread of the disease is recommended through condom use or monogamous sexual relations.