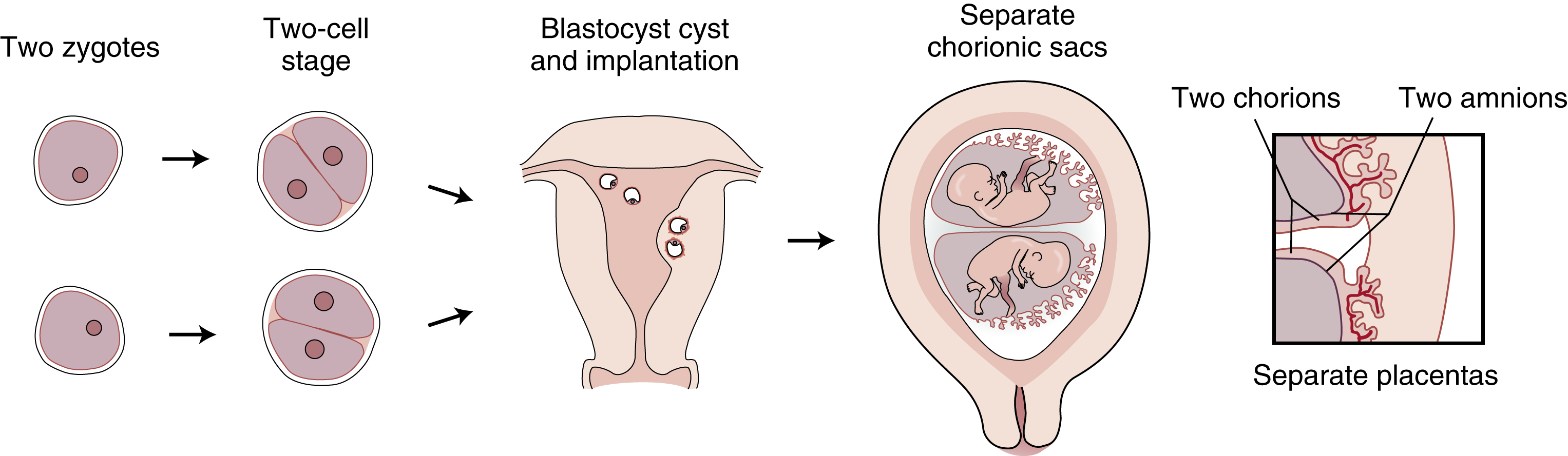
dizygotic twins, two offspring born of the same pregnancy and developed from two ova that were released from the ovary simultaneously and fertilized at the same time. They may be of the same or opposite sex, differ both physically and genetically, and have two separate and distinct placentas and membranes, both amnion and chorion. The frequency of dizygotic twinning varies according to ethnic origin (the highest incidence occurs in African-Americans, the lowest in Asian-Americans, with Caucasians intermediate), maternal age (the highest rate occurs when the mother is 35 to 39 years of age), and heredity (showing an increase in the female genetic line rather than the male, although fathers may transmit the disposition to double ovulation to their daughters). In general the overall ratio is two thirds dizygotic twinning to one third monozygotic. Also called binovular twins, false twins, fraternal twins, heterologous twins, dissimilar twins.