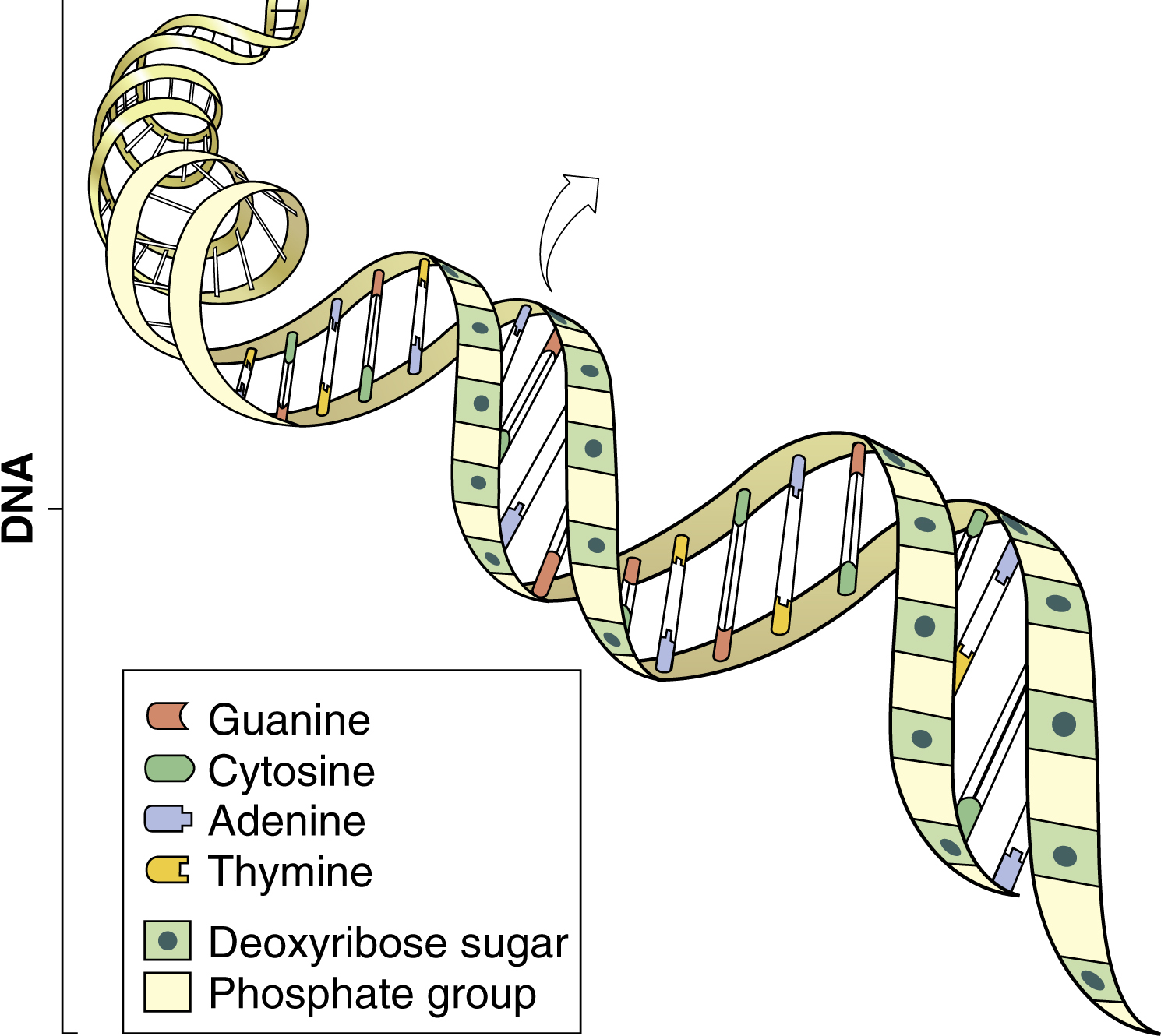
deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) /dē·ok′sirī′bōno̅o̅klē″ik/ , a large, double-stranded, helical molecule that is the carrier of genetic information. In eukaryotic cells, it is found principally in the chromosomes of the nucleus. DNA is composed of four kinds of serially repeating nucleotide bases: adenine, cytosine, guanine, and thymine. Genetic information is coded in the sequence of the nucleotides. See also nucleic acid, ribonucleic acid.