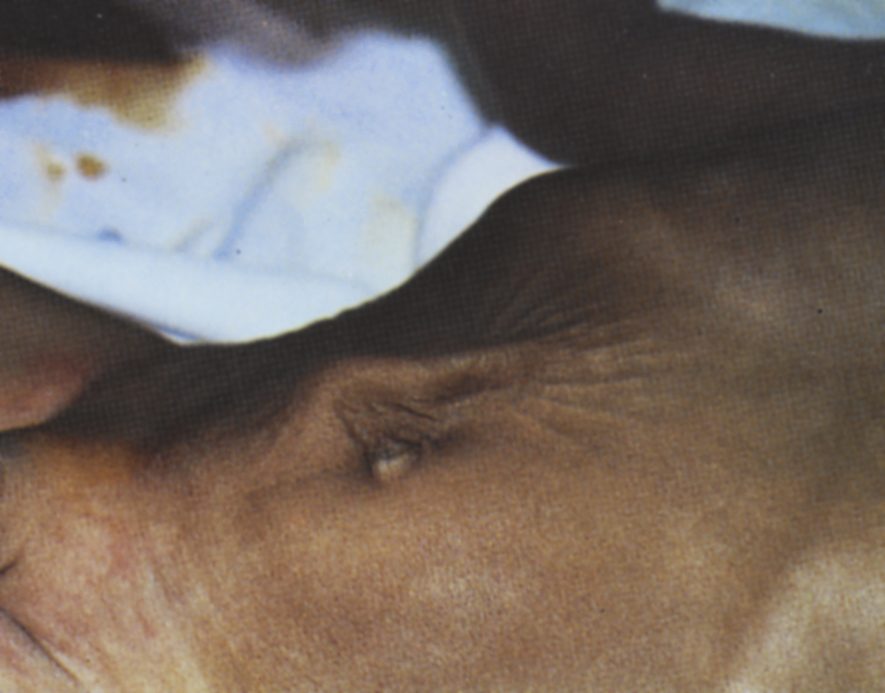
dehydration /di′hīdrā″shən/ , 1. excessive loss of water from body tissues. Dehydration is accompanied by a disturbance in the balance of essential electrolytes, particularly sodium, potassium, and chloride. It may follow prolonged fever, diarrhea, vomiting, acidosis, and any condition in which there is rapid depletion of body fluids. It is of particular concern among infants, young children, and the frail elderly because their electrolyte balance is normally precarious. Signs of dehydration include poor skin turgor (not a reliable sign in the elderly), flushed dry skin, coated tongue, dry mucous membranes, oliguria, irritability, and confusion. Normal fluid volume and balanced electrolyte values are the primary goals of therapy. 2. rendering a substance free from water. Also called anhydration.