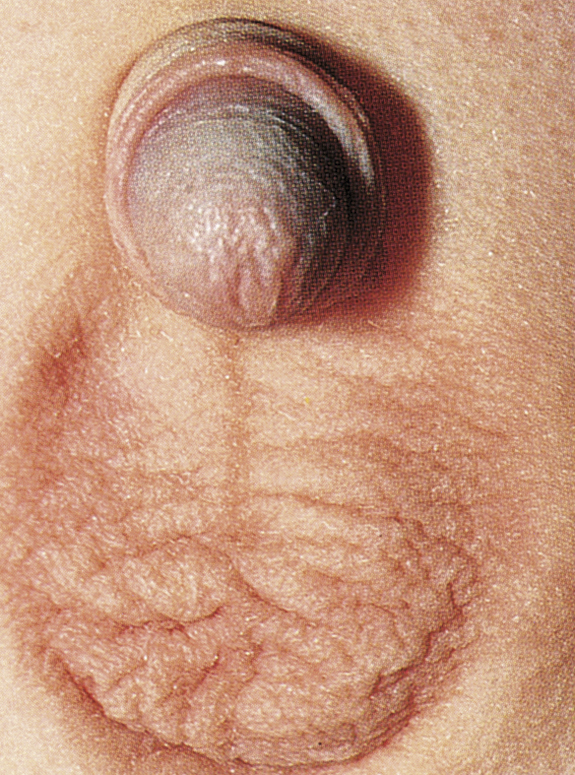
cryptorchidism /kriptôr″kidiz′əm/ [Gk, kryptos, hidden, orchis, testis] , a developmental defect in which one or both testicles fail to descend into the scrotum and are retained in the abdomen or inguinal canal. The testes normally migrate into the scrotal sac at birth, but normal testicular descent depends on timely and synchronous development of other embryonic structures. If spontaneous descent does not occur by the age of 1 year, hormonal injections may be given. If injections are unsuccessful, orchiopexy is usually performed before age 3. Also called cryptorchid testis, undescended testis, cryptorchis.